What is Cardiovascular Disease
(DVD)
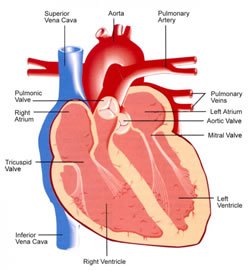
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a general term used to describe disorders that can
affect the heart (cardio) and /or the body's system of blood vessels (vascular).
Most cardiovascular diseases reflect chronic conditions – conditions that develop or persist
over a long period of time. However, some of the outcomes of cardiovascular disease may be
acute events such as heart attacks and strokes that occur suddenly when a vessel supplying
blood to the heart or brain becomes blocked.
Risk Factor
Cardiovascular diseases occur more frequently in people who smoke, who have high blood
pressure, who have high blood cholesterol (especially high LDL-C), who are overweight,
who do not exercise, and/or who have diabetes. Therefore, public health initiatives
focus on decreasing CVD by encouraging people to:
- Follow a healthy diet
- Avoid smoking
- Exercise regularly
- If diabetic, maintain good control of blood glucose
- Conduct periodic diagnosis / tests
In addition, there are some risk factors that cannot be controlled, including age, gender
& family history:
- CVD risk increases with age.
- Men are generally at higher risk of heart disease; however, women's risk increases
to that of men's after menopause.
- Having a first-degree relative who had coronary heart disease or a stroke before age
55 for a male relative or before after 65 for a female relative increases the risk.
Types
Some of the classifications of CVD include:
- Coronary heart disease (CHD) and coronary artery disease (CAD) – disease of the
blood vessels supplying the heart that may lead to:
- Angina
- Heart attack
- Congestive heart failure
- Cerebrovascular disease – disease of the blood vessels supplying the brain that
may lead to:
- Transient ischemic attacks (TIA) or "mini strokes"
- Strokes
- Peripheral vascular disease – disease of blood vessels supplying the arms and
legs that can lead to:
- Claudication – obstructed blood flow in arteries, causing pain
- Gangrene – death of tissues in legs due to poor circulation
- Aneurysms
Other types of disease can also affect the heart and/or blood vessels. These are
described in more detail in the Heart Disease and Vasculitis articles and include:
- Congenital heart disease – resulting from malformation of the heart structure
during development (includes some valvular diseases)
- Valvular disease – defects in the structure or function of a heart valve; may be
either congenital or acquired
- Cardiomyopathy – weakening of the heart muscle
- Myocarditis – inflammation or infection of the heart muscle
- Vasculitis – inflammation of blood vessels
- Blood clots that develop in the veins (thrombosis) and that detach and go to
other organs (embolism)
- Atrial fibrillation – quivering or irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) that can
lead to blood clots, stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related
complications
The World Health Organization estimates that cardiovascular diseases represent 30% of
all global deaths. Over 80% of deaths from CVD occur in low- and middle-income
countries, where there is increased exposure to risk factors and less access to
preventive measures and adequate health care. As the leading cause of death
worldwide, cardiovascular disease is a focus of international interest
Laboratory Tests
A variety of blood tests are available to help diagnose and/or monitor your Cardiac
health.
Stay Connected!
Get our
Newsletter delivered to your inbox!
Nucleus The Diagnostic centre is the unique diagnostic centre
providing clinical pathology services to the citizens of
Kalyan-Dombivali area, Established in year 2006 by Atul S. Vadhavkar
and Dr. Aniruddha J. Ranadive, we are functioning
till this date without a single holiday.
We are the only
clinical pathology laboratory working 24x7 in truly professional
manner keeping pace with time in terms of upgrading techniques and
technology.
We provide
vital support to hospitals and out patients in the fields of
clinical pathology, histopathology, biochemistry, immunoassays,
microbiology and other related fields. Soon venturing in field of
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
testing.

Science of haematology deals with blood and it’s components. It
speaks of haemoglobin, Red Blood Cells, White Blood Cells,
Platelets, size and structure of cells and abnormalities of Them.
Haemoglobin: It is most important part of blood as it supplies
Oxygen to all tissues of body. If for any reason somebody lacks
proper haemoglobin level, which is called as anaemia, it causes
serious problems such as breathlessness, swelling on body, paleness
and even serious cardiac problems. Deficiency of haemoglobin can be
due to many reasons. Some are lack of proper diet, iron deficient
diet, vitamin deficiencies and some hereditary causes. WBCs are very
important in defence mechanism of body. They try to kill the
invaders and keep body protected. It is very important to know about
blood parameters to fight diseases and maintaining health.

Microbiology is branch of biology which deals with microorganisms and
clinical microbiology deals with microorganisms responsible for
diseases. In laboratory, suspected samples such as pus from wounds
or secretions, body fluids such as blood, Cerebrospinal fluids,
pleural fluids are inoculated in enrichment media where the
microorganism such as bacteria and fungi can grow fast and freely.
Now with state of the art automated equipment help to identify the
type of organism causing disease faster and further lets us know
which antibiotics will efficiently kill them.

This branch of science which deals with chemical reactions and
variation in metabolic activities of body. For example diabetes can
be detected by performing blood sugar test from blood sample of
suspected patient. If found values higher then expected normal
values, patient can be kept on diet control and medicines.
Persistent high values of Cholesterol and Triglycerides in blood may
lead to atherosclerosis or blockage of blood vessels and there after
serious cardiac dysfunctions or myocardial infarctions. Altered
levels of electrolytes namely Sodium, Potassium, Calcium, Chloride
can cause serious problems like fainting or unconsciousness. In
certain liver problems enzymes like S.G.O.T. and S.G.P.T., Alkaline
phosphatase are raised in serum. Bilirubin is found raised in cases
of jaundice. These can be detected from blood samples. Renal
problems can be detected by testing blood for increased levels of
creatinine and urea in serum. Decisions can be made for procedures
like dialysis just by blood test. Raised levels of cardiac enzymes
like CK-NAC, CK-MB, LDH, S.G.O.T. give idea about status of heart in
case of myocardial infarctions. It helps understanding deficiencies
and replenishing of biochemicals of human body.

Clinical pathology is a medical specialty that is concerned with the
diagnosis of disease based on the laboratory analysis of bodily
fluids, such as blood, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, stool etc. It
helps diagnosing abnormalities in digestive system, urinary tract,
cerebrospinal system etc.

This specialized branch of pathology deals with surgically removed
parts of body and Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology. The parts of body
which are removed from body after surgery, are sent for
histopathological studies. These parts are made in to wax blocks and
then very thin sections are done with the help of microtome. These
sections are stained and mounted on glass slides. The sections thus
taken are examined under microscope for abnormalities, unwanted
growth and cancers. F.N.A.C.s are performed by aspirating fluids or
other contents of enlarged or swollen glands or bulges. These
aspirated materials are taken on glass slides, stained and observed
under microscope for abnormalities, tuberculosis or cancers.

An Immunoassay is a biochemical test that measures the presence or
concentration of a macromolecule in a solution through the use of an
antibody or immunoglobulin. The macromolecule detected by the
immunoassay is often referred to as an "analyte" and is in many
cases a protein. Analytes in biological liquids such as serum or
urine are frequently measured using immunoassays for medical and
research purposes. This branch mainly deals with hormones and their
imbalances. These hormones are secreted in body in very small
amounts but are very essential to keep chemical and mechanical
cycles of healthy human body to be carried out smoothly. Imbalances
in these hormones can cause severe health problems.
>